AD
AD
Country
- Africa
- Alcohol, Tobacco & Drugs
- Animals, Fish, Insects & Birds
- Anniversaries
- Australia
- Books
- Brazil & S.America
- Buddhism
Category
- Afghanistan, AF
- Aland Island, AX
- Albania, AL
- Algeria, DZ
- American, Samoa, AS
- Andarra, AD
- Angola, AO
- Anguilla, Al
Event Type
- Daily
- Weekly
- Annual
- Recurring
Duration
- All
- 1 Day
- 2 Day
- 3 Day
- 4 Day
- 5 Day
- 6 Day
Event Type
- Daily
- weekly
- Annual
- Recurring
Event Type
- Daily
- weekly
- Annual
- Recurring
Today is: October 18
Beard Day (No)
Birth of the Bab (1819)
Bridge Day Festival, Fayetteville, (US-WV)
Chocolate Cupcake Day
Dhanteras (H)
Fetch Day, Ntl.
Independence Day Holiday, (AZ)(1991)
Menopause Day, World
Opossum Day, Ntl. (CA)
Oyster Festival US, Leonardtown (US-MD)
Person's Day (CA)(1929)
Saint Luke Feast Day
Sloth Day, Intl
Squash Day, World
Sweetest Day
Wales International Film Festival
Black in Natural History Museums Week
Bone and Joint Action Week, Ntl.
Bullying Bystanders Unite Week
Character Counts Week, Ntl.
Chemistry Week, Ntl.
Coffee Week, (UK)
Diwali (Deepavali) (H)
Felabration (NG)
Food and Drug Interaction Education Week
Foot Health Week (AU)
Forest Products Week, Ntl.
Friends of Libraries Week, Ntl.
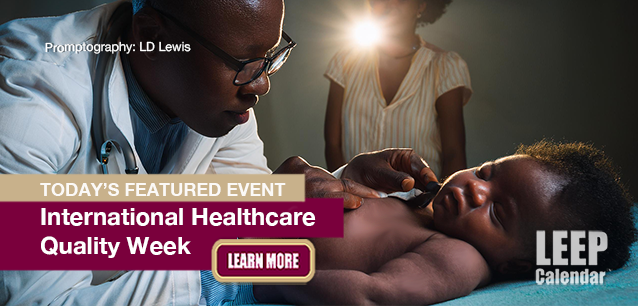
Healthcare Quality Week, Intl.
IMF World Bank Summit (US-DC)
Lead Poisoning Prevention Week of Action, Intl.
Male Breast Cancer Awareness Week, Ntl.(US/CA/AU)
Massage Therapy Week, Ntl.
Minority Enterprise Development Week, Ntl.
Newspaper Week (JP)
Pastoral Care Week
Pet Obesity Week, World
Recycle Now Week (UK)
Recycle Now Week (UK)
Recycle Week, Ntl. (UK)
Red Bull Tuk Tuk Tournament (LK)
Respiratory Care Week, Ntl.
Retirement Security Week, Ntl.
Rodent Awareness Week, Ntl.
School Safety Week, Ntl (CA)
Schools Week, America's Safe
Sock it to Suicide Week (AU)
Storytelling Festival, Scottish Intl. (UK)
Stuttering Awareness Week, Intl.
Teen Driver Safety Week, Ntl.
Towns Week, Ntl. (PH)
Urban Wildlife Week, Intl.
Veterans' Health Week (AU)
Wolf Awareness Week, Intl
World Series MLB
ADHD Awareness Month
Adopt-a-Dog Month, (AHA)
Adopt-a-Shelter Dog Month
Alcohol Awareness Month, Collegiate Ntl.
Animal Safety and Protection Month, Ntl.
Antidepressant Death Awareness Month
Anxiety and Depression Awareness Month (AU)
Apple Month, Ntl.
Applejack Month
AquaTober
Architecture Month, Archtober
Arts and Humanities Month, Ntl.
Audiology Awareness Month, Ntl.
Autism Awareness Month (CA)
Bake and Decorate Month, Ntl.
Bat Appreciation Month
Battery Safety Month (Auto)
Bi-national Health Week (US/CA/MX-varies locally)
Big Draw, The
Bilingual Child Month, Celebrating the
Black History Month (UK)
Black Speculative Fiction Month
Bleeding Disorders Month, Ntl. (AU)
Blind Month, National Meet the
Blindness Awareness Month
Book Month, Ntl.
Breast Cancer Awareness Month, Ntl.
Bullying Month, Stop, Ntl.
Bullying Prevention Month, Ntl.
Caffeine Addiction Recovery Month
Car Care Month, Ntl. Fall
Caramel Month, Ntl.
Celiac Awareness Month (US)
Cheese Month, American
Chili Month, Ntl.
Chiropractic Health Month, Ntl.
Church Library Month
Church Safety and Security Month, Ntl.
Class Reunion Month
Clergy Appreciation Month
Co-op Advertising Awareness Month
Co-op Awareness Month
Company Culture Month, Global
Company Culture Month, Global
Computer Learning Month
Contact Lens Safety Month
Cookie Month
Corn Month
Country Ham Month
Country Music Month
Crime Prevention Month, Ntl.
Critical Illness Awareness Month
Cybersecurity Month, Ntl.
Danger Run (US-KY, IN, IL)
Dental Hygiene Month, Ntl.
Depression Education and Awareness Month
Dessert Month, Ntl.
Disability Employment Awareness Month
Diversity Awareness Month, Global
Domestic Violence Awareness Month
Down Syndrome Month, Ntl.
Dyslexia Awareness Month
Eat Better—Eat Together Month
Eczema Awareness Month
Emotional Intelligence Awareness Month
Energy Action Month, Ntl.
Ergonomics Month, Ntl.
Eye Injury Prevention Month
Fair Trade Month
Family History Month
Festival of Penha (BR-RJ)
Filipino American History Month (1587)
Financial Planning Month
Freethought, Month of, Ntl.
Gain the Inside Advantage Month, Ntl.
Gay and Lesbian History Month (1979)
German-American Heritage Month (1683)
Girls Night In (AU)
Go Sober Month (UK)
Golf Month, Australia
Great Cycle Challenge (AU)
Halloween Safety Month
Head Start Awareness Month
Health Literacy Month
Healthy Lung Month
Healthy Workplace Month (CA)
Hog-out Month (US-TX)
Home Eye Safety Month
Indigenous Peoples Month, Ntl. (PH)
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) Month, Ntl.
Islamic History Month (CA)
Italian-American Heritage Month (1492)
Kartika (H)
Katik (S)
Kitchen and Bath Month, Ntl.
Learning Disabilities Month, Ntl. (CA/US)
Learning and Development Month, Ntl.
Liver Awareness Month, Ntl.
Long Term Care Planning Month
Lupus Awareness Month (UK)
Medical Librarians Month, Ntl.
Medicine Abuse Awareness, Ntl.
Menopause Month, World
Museums and Galleries Month (PH)
Muslim American Heritage Month (US)
Non-GMO Month, Ntl.
Organize Your Medical Information Month
Orthodontic Health Month, Ntl.
Pasta Month, Ntl.
Pedestrian Safety Month
Pescatarian Month, Ntl.
Pet Wellness Awareness Month, Ntl.
Pharmacist Month, American
Photographer Appreciation Month
Physical Therapy Month, Ntl.
Pickled Peppers Month
Pink Ribbon Breakfast (AU)
Pit Bull Awareness Month, Ntl.
Pituitary Awareness Month (UK)
Pizza Month, Ntl. (1984)
Polio Awareness Month, (CA/AU)
Polish-American Heritage Month
Popcorn Poppin' Month, Ntl.
Positive Attitude Month
Prenatal-onset GBS Disease Recognition Month
Pretzel Month, Ntl.
Principal's Month, Ntl.
Protect Your Hearing Month, Ntl.
Rabi al-Thani (M)
Reading Group Month, Ntl. (1917)
Rett Syndrome Awareness Month
Roller Skating Month, Ntl.
STEM Mentoring Month
Sarcastic Awareness Month
Sausage Month, Ntl.
School Libraries Month, Intl.
Seafood Month
Seed Gathering Seasons (UK)
Senior's Month (AU-QLD)
Sensory Awareness Month, Ntl.
Shoctober - Defibrillator National Awareness Month (AU)
Spina Bifida Awareness Month, Ntl.
Spinach Lovers Month
Spinal Health Month, Ntl.
Squirrel Awareness and Appreciation Month
Stamp Collecting Month, Ntl
Stop America's Violence Everywhere (SAVE) Month
Substance Abuse Preservation Month, Ntl.
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) Awareness Month
Sunday School Teacher Appreciation Month
Teentober
Tishrei (J)
Turner Prize Exhibition (UK)
U.S.-Mexico Border Health Month
Ultrasound Awareness Month
Unblocktober (UK)
Urban October
Vegetarian Month
Walk To School Month, Intl.
Wild About Gardens Week (UK)
Window Covering Safety Month, Ntl.
Winter Weather Preparedness Weeks (Varies by Location)
Wishbones for Pets (US/CA)
Women's History Month (CA)
Women's Small Business Month
Work and Family Month, Ntl.
Workplace Politics Awareness Month
Youth Justice Action Month, Ntl.
LEEP Calendar
Scroll to explore events active on this date.
LEEP INK FEATURES

August? Absolutely!
In August, we live through the Dog Days of Summer. It's hot and often humid, and those who can leave for better climates do. Down south, winter is in full force. August is also known as "the ...

In The Heat of July: July 2025 Events
Is it hot enough (or cold enough if you're below the equator) for you yet? There is actually a day for that! Like every month, I pick a diverse collection of events you may or may not know about. This ...

May Blooms: Events in May 2025
Along with October, May is one of the most densely packed months of the year. It's before the summer humidity and the last whole month of the school year. The weather is warming in t...
About the Snap Election in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom & Ireland
Ends: Jul 04, 2024
DESCRIPTION:
SNAP ELECTION IN THE UNITED KINGDOM
Prime Minister Rishi Sunak announced on May 22, 2024, that a British snap election will be held on July 4, 2024. This election will determine the composition of the House of Commons and the United Kingdom's next government.SNAP VS GENERAL ELECTION
The prime minister is required to call a general election by the end of autumn 2024. Rather than wait until November, Sunak called for a snap election in July. What is the difference between a general election and a snap election?
GENERAL ELECTION
a) Regularly Scheduled: General elections occur regularly, usually every five years.
b) Purpose: They are used to elect Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons to form a new government.
c) Predictable: The general election date is typically known well in advance, allowing for a standard election campaign period.
SNAP ELECTION
a) Called Early: Often unexpectedly, Snap elections are called before the fixed term's end.
b) Triggering circumstances include:
c) Purpose: Like general elections, snap elections also elect MPs to the House of Commons and aim to form a new government, but they occur outside the regular election cycle.
d) Less Predictable: The timing of snap elections is often a strategic decision by the government, catching opposition parties and the electorate off guard.
Both snap and general elections serve the same fundamental purpose of electing MPs and forming a government; their key differences lie in their timing and the conditions under which they are called.CURRENT POLITICAL LANDSCAPE
In addition to the two largest parties, Labour and Conservatives (Tories), the United Kingdom includes several influential political groups vying for seats in parliament. Many will win a small minority of available seats. However, early polling data favor Labour to win the most seats in July, with voters citing fatigue and frustration over various policies and positions under the past two decades of Conservative leadership.
The July snap election evolved amid these various political challenges and may significantly reshape the United Kingdom's political landscape. Following the election, the party with the most seats in the House of Commons will choose the next prime minister, which the sovereign may then accept or reject. UNITED KINGDOM GOVERNMENT STRUCTURE 101
The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy, with the sovereign (Crown) as head of state.
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is bicameral (two chambers): the House of Lords and the House of Commons. Together, they legislate.
The House of Lords includes hereditary membership and Crown appointees.
The House of Commons is elected every five years. It represents the people and has the most collective power.
Laws are created in the Commons and approved in the Lords.
The Prime Minister is a member of the House of Commons. As a parliamentarian-style government, coalitions are formed after elections, giving less popular parties winning seats in the Commons a say and influence in how the government runs and the laws of the land.
The British election cycle is typically six weeks.
VIDEOS
SUPPORTING DOCUMENTS
Currently, this event does not have supporting documents.
ADDITIONAL IMAGES
Currently, this event does not have supporting images.
Where would you like to go now?
 AD
AD
By using this site. You are agreeing to use of cookies. Learn more in our Privacy Policy
/footer-logo.svg)
LEGAL: Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear attribution is given to Jubilee LLC and LEEPCalendar.com, with appropriate and specific direction to the original content (Page URL). Additional documents, embedded videos and additional image rights retained by their creators and are provided to increase understanding of the event or topic.
Jubilee LLC reserves the right to accept or reject inclusion of events in this calendar. The appearance of an event in LEEP Calendar does not imply endorsement of the event, nor the organization championing the event by Jubilee LLC, its stakeholders, customers or subsidiaries. All dates, contact information, URLs, addresses, and information relating to any event, promotion or holiday are subject to change without notice and should be treated as estimated. Jubilee LLC, our stakeholders, customers and subsidiaries cannot warrant accuracy. Users of this application are solely responsible for verifying actual event date with organizers and additional sources prior to committing resources, financial, human or otherwise.